TARSAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
Definition
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome (TTS) occurs when the tibial nerve in the foot becomes pinched. Tarsal – referring to the lower ankle and Tunnel referring to the structure within the ankle is an area that contains different nerves, blood vessels and tendons. When the tibial nerve becomes pinched or constricted, inflammation and pain can ensue. This condition is similar to the carpal tunnel syndrome in the wrist.
Symptoms
The pain of TTS can be severe. It is usually characterized as an aching, burning pain that radiates throughout the ankle, heel, and even to the toes of the foot. Pain usually subsides after weight has been removed from the ankle. However, often pain can be the worst during the night when sleeping.
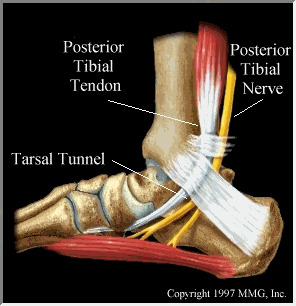
Relevant Anatomy
The tarsal tunnel is a structure in the foot formed between the underlying bones of the foot and overlying fibrous tissue. The flexor retinaculum constitutes the roof of the tarsal tunnel. The tibial nerve passes behind the inside part of the ankle and through the tarsal tunnel and splits into several branches. The main divisions of the tibial nerve include the calcaneal, medial plantar, and lateral plantar nerve branches. The medial plantar nervepasses to supply the first three toes. The lateral plantar nerve travels to supply the outside two toes and tissues. Calcaneal branch goes to inside and posterior aspects of the heel.
Causes
TTS can result from a number of conditions. Pronation (inward rolling of the foot and ankle) can be one cause. Another cause of TTS is arthritis which can cause inflammation in the joint of the ankle and lead to damaged nerves in ankle. Heel Spurs are also a cause of this condition, either by direct effect of the tibia nerve or changes in gait. Obesity is also a common cause that will put added stress on the joint and structures of the ankle. Other causes of compression include: lipomas, tendon sheath ganglia, neoplasms within the tarsal canal, nerve sheath and nerve tumors, and varicose veins.
Treatment
Simple rest or massages can relive some pain associated with this condition. Other treatment methods include cortisone injections and physical therapy. Among the most widely used treatment method for TTS is the use of an orthotic. An orthotic is a simple device that is inserted into the shoe. Surgery may also be a possible treatment method.
Testing
Electromyography (EMG/NCS) and nerve conduction (NCV) studies may be a useful tool in evaluating suspected cases of TTS. The presence of neuropathy can be confirmed. Additionally, the type of nerve fiber (sensory, motor, or both) and the physiology (axonal vs demyelinating) can be determined. A normal test result does not exclude the diagnosis of TTS.

Contact Us
13710 Olive Boulevard (Primary Office)
Chesterfield, MO 63017
Telephone: 314-469-PAIN (7246)
Fax: 314-469-7251
Exchange: 314-441-6965 (for after-hour Emergencies Only)
Hours:
Monday thru Friday
8:30 AM – 4:30 PM

